Monday, November 29, 2010
Negative feedback
Thrombin bound to thrombomodulin activates protein C, an inhibitor of the coagulation cascade. The activation of protein C is greatly enhanced following the binding of thrombin to thrombomodulin, an integral membrane protein expressed by endothelial cells. Activated protein C inactivates factors Va and VIIIa. Binding of activated protein C to protein S leads to a modest increase in its activity. Thrombin is also inactivated by antithrombin, a serine protease inhibitor
12
下列關於輔脂酶(colipase)之敘述,何者正確?
位於小腸上皮細胞膜上
負責消化三酸甘油酯(triglycerides)
可將脂肪酶原(prolipase)轉化成脂肪酶(lipase)
避免脂肪酶(lipase)受到膽鹽的影響而降低其活性
D
Mode of Action
[edit]Hirsutism
Eflornithine topically applied is an irreversible inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), an enzyme that catalyses the conversion of ornithine to putrescine, which plays an important role in cell division and proliferation in the hair follicle.[11]
[edit]Sleeping sickness treatment
Eflornithine appears to kill trypanosomes by acting as a suicide inhibitor of the enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.17). This enzyme regulates cell division by catalysing the first step in polyamine biosynthesis. As the inhibitor has a low half-life in humans, it is broken down rapidly while the parasite cannot metabolise it quickly enough. This means that it preferentially harms the parasite.
Sunday, November 28, 2010
Anatomy
[edit]Regions
The vascular middle layer of the eye. It is traditionally divided into 3 areas, from front to back, the iris, ciliary body, and choroid.
36
具有「膠質原纖維酸性蛋白(glial fibrillar acidic protein, GFAP)」的細胞是:
星狀膠細胞(astrocyte) 腦室襯裏細胞(ependymal cell)
寡突膠細胞(oligodendrocyte) 微膠細胞(microglia)
A
37
下列有關牙齒的敘述,何者正確?
星形網(stellate reticulum)是由間葉(mesenchyme)衍生而來
琺瑯質(enamel)是由外胚層(ectoderm)衍生而來
齒質(dentine)是人體中最硬的構造
琺瑯質先形成之後,齒質再形成
B
38
破骨細胞(osteoclast)較常出現的區域是:
骺板細胞增殖區(zone of cell proliferation)
骺板細胞肥大和軟骨鈣化區(zone of hypertrophy and calcification)
骺板軟骨儲備區(zone of reserve cartilage)
骺板骨化區(osteogenic zone)
D
39
下列那一細胞層,僅出現在手掌或腳掌之厚皮膚?
角質層(stratum corneum) 透明層(stratum lucidum)
顆粒層(stratum granulosum) 棘狀層(stratum spinosum)
B
THICK SKIN: LUCIDUM!!!
43
下列何者無法培養在一般的大氣中?
霍亂弧菌(Vibrio cholerae) 綠膿桿菌(Pseudomonas aeruginosa)
志賀氏赤痢菌(Shigella dysenteriae) 幽門桿菌(Helicobacter pylori)
D
47
梭狀芽孢桿菌屬(Clostridium)病菌生存時不會產生下列何種毒素?
腸毒素(enterotoxins) 神經毒素(neurotoxins)
溶組織毒素(histolytic toxins) 內毒素(endotoxins)
D
54
輪狀病毒(Rotavirus)和挪瓦克病毒(Norwalk virus)屬於不同病毒,但它們共同具有下列何種特性?
可經由糞-口傳播 均是雙股RNA 均是單股RNA 可經由游泳傳播
A
56
下列關於病毒與其引起之疾病的敘述,何者為錯?
狂犬病毒(Rabies virus)可引起恐水症(hydrophobia)
B型克沙奇病毒(Coxsackie B virus)可引起胸膜痛(pleurodynia)
輪狀病毒(Rotavirus)可引起嬰兒腹瀉(infantile diarrhea)
A型克沙奇病毒(Coxsackie A virus)可引起出血熱併腎症候群(hemorrhagic fever with renal
syndrome)
D
COX B: BLEURODYNIA!!!!
The most well known Coxsackie A disease is Hand, foot and mouth disease (unrelated to foot and mouth disease),
What is hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome? ![]()
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) is a group of clinically similar illnesses caused by hantaviruses from the family Bunyaviridae. HFRS includes diseases such as Korean hemorrhagic fever, epidemic hemorrhagic fever, and nephropathis epidemica. The viruses that cause HFRS include Hantaan, Dobrava-Belgrade, Seoul, and Puumala.
Passages
The following passages connect the fossa with other parts of the skull:
Direction | Passage | Connection |
| Posteriorly | foramen rotundum | middle cranial fossa |
| Posteriorly | pterygoid canal (Vidian) | middle cranial fossa, foramen lacerum |
| Posteriorly | palatovaginal canal (pharyngeal) | nasal cavity/nasopharynx |
| Anteriorly | inferior orbital fissure | orbit |
| Medially | sphenopalatine foramen | nasal cavity |
| Laterally | pterygomaxillary fissure | infratemporal fossa |
| Inferiorly | greater palatine canal (pterygopalatine) | oral cavity, lesser palatine canals |
Contents
The deep perineal pouch contains:
- muscles
- other
- Membranous portion of the urethra (males) / proximal portion of urethra (females)
- Bulbourethral gland (males). (Note: The Bartholin gland is the female counterpart to the bulbourethral gland in males, but it is located in the superficial perineal pouch.)
- Vagina (females)
Innervation and vascular supply
The cremaster muscle is innervated from the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve and supplied by the cremasteric artery.
It receives distinctly different innervation and vascular supply in comparison to the internal oblique.
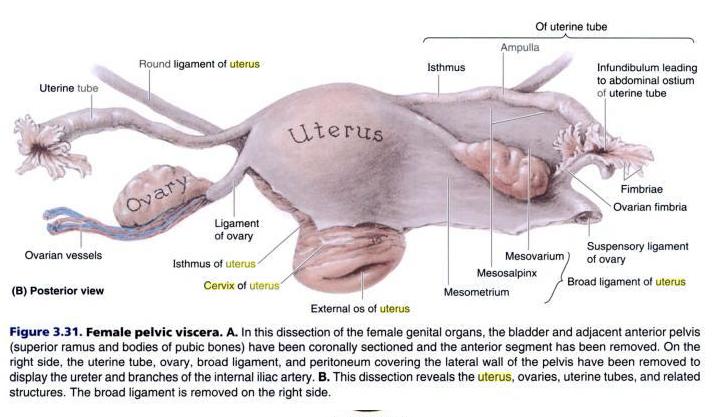
The suspensory ligament of the ovary, also infundibulopelvic ligament (commonly abbreviated IP ligament or simply IP), is a fold of peritoneum[1] that extends out from the ovary to the wall of the pelvis.
Some sources consider it a part of the broad ligament of uterus[2] while other sources just consider it a "termination" of the ligament.[3]
The suspensory ligament is directed upward over the iliac vessels.
 5
5Between the styloid and mastoid processes of the temporal bone is the stylomastoid foramen
It is the termination of the facial canal, and transmits the facial nerve and stylomastoid artery.
Contents
Several nerves, arteries and veins pass through the foramen ovale. They are as follows:
- Mandibular nerve (the third branch (V3) of the trigeminal nerve)
- Accessory meningeal artery (small meningeal or parvidural branch, sometimes derived from the middle meningeal artery)
- Lesser petrosal nerve of (CN IX) (note: the lesser superficial petrosal nerve sometimes passes through a special canal (canaliculus innominatus of Arnold), situated medial to the foramen spinosum)
- Emissary veins (from the cavernous sinus to the pterygoid plexus)
- The otic ganglion is situated directly under the foramen, but is also transmitted through the foramen ovale.
The contents of this foramen neatly form the mnemonic 'OVALE' (otic ganglion, V3, accessory meningeal artery, lesser petrosal nerve, emissary veins)
